Describe the Protective Mechanism of Skin
Bloodstream macrophages mature tissue Chemotaxis. Changes in temperature and humidity.
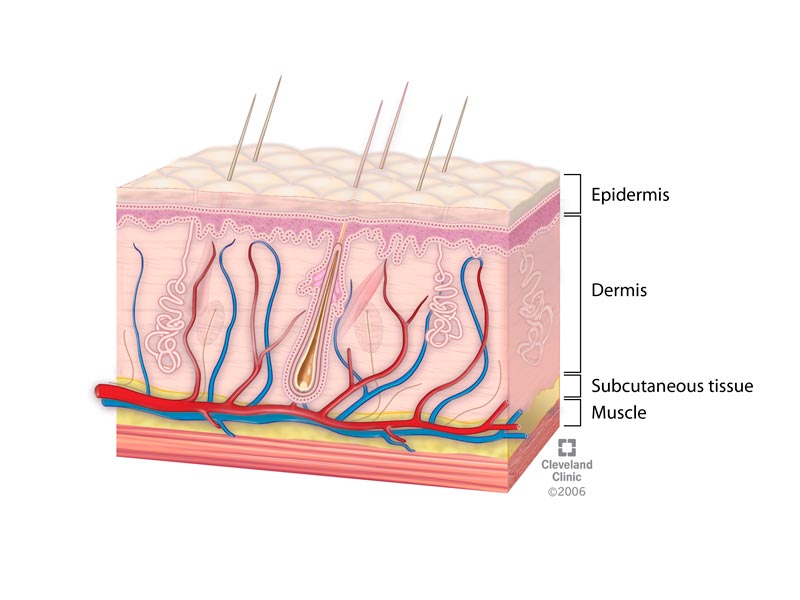
Skin Layers Structure And Function
The brain is the best protected organ in the body.

. The cellular components include cells of the immune system and the vascular endothelium. These mechanisms include increasing epidermal thickness DNA repair mechanisms and apoptosis antioxidant enzymes and last but not least skin pigmentation. Protection The outermost layer of your skin the epidermis is the thin tough part of your body that acts like a protective shell.
Protects against UV radiation by melanin pigments produced by melanocytes in the epidermis and dermis. Sebum unsaturated fatty acids provides a protective film on the skin and inhibits growth. Melanin pigmentation and the evolution of dark skin is an adaptive protective mechanism against high levels of UVR exposure.
The next layer of defence is the lymphatic system situated superficially just. The skin serves as a wall-like barrier that separates the inside of our body from the microbial enemies of the environment and provides a primary defense against infection. Stratum cornea - Epidermis - Papillary edema - Reticular dermis - Hypodermis.
The many external factors that skin protects us from include. Conreacytes Keratinocytes Melanocytes Tight Junctions. Jablonski explains that melanin located in the top layer of human skin absorbs UV radiation protecting cells from the damaging effects of UV.
12 The layers of the skin like the outer wall and secondary inner walls surrounding a medieval city not only provide protection from external enemies but also provide niches where normal flora bacteria. The protective mechanisms of the body begin with the architecture of the epithelial surfaces. A localized concentration of melanin.
This is a complex integrated response with multiple components including cellular and humoral. Pigment that contributes to skin color. The skin is a stratified keratinized squamous epithelium.
Skin helps to regulate body temperature control moisture loss and maintain the. UV light stimulation of skin results in the production of vitamin. A Survey and Systematic Review.
When the immune system is activated an inflammatory response is engaged as a protective mechanism. Microbes are detected by toll-like receptors while interferons form the first line of. The bodys outer surfaces produce chemicals which are bactericidal skin is shed and membranes expectorate mucous in order to expel pathogens.
Particles bacteria and dead or dying cells. The air that organisms breathe contains particulate matter such as dust dirt viral particles and bacteria that can damage the lungs or trigger allergic immune responses. Mucous membranes line the various body cavities that open to the exterior.
Hyaluronic acid is a gelatinous substance that slows the spread of noxious agents. Insulates cushions underlying body tissues. The literature also shows that essential biomechanical information of the sliding event is.
Acidity on skin inhibit bacterial growth. According to certain chemicals in their environment. Skin appendages are derived from the skin and include hair nails and glands.
The skin preserves the bodies homeostasis by regulating temperature and water loss while also serving both endocrine and exocrine functions. In the film Dr. First by inducing pigment synthesis in melanocytes MC1R enhance production and accumulation of eumelanin in the epidermis.
Melanin helps protect the cells of the epidermis or outer layer of the skin from UV light. The mucous membrane of the bladder. The protective mechanisms of the body collectively form part of the innate immune system.
Because theyre also the first to encounter damage the cells of the epidermis are constantly renewing themselves with dead skin cells falling off by the tens of thousands each minute. Four protective functions of the skin. Kertanized matrix with dead cells.
Ingesting phagocytosing harmful foreign. Understanding the Acute Skin Injury Mechanism Caused by Player-Surface Contact During Soccer. Genetics determines the type of melanin ie brownblack eumelanin or redbrown pheomelanin and the amount of melanin present in an individuals cells.
Protective mechanisms of the body Skin Figure 2. Commensals or non-pathogenic bacteria further inhibit growth by competing for space and nutrients on the bodys skin and mucous membrane linings. Phenomenon in which cells direct their movements.
There is a basal layer of keratocytes which. Skin is the first site of immunological defense by the action of the Langerhans cells in the epidermis which are dendritic epidermal T lymphocytes and part of the adaptive immune system. MC1R signaling protects the skin from UV damage by at least two major mechanisms.
Nonspecific Resistance Innate Immunity. One of its primary roles is protection against exposure to sunlight a major source of skin damage where the UV radiation UVR component functions as a complete carcinogen. The respiratory system contains several protective mechanisms to avoid problems or tissue damage.
This article will describe some of these protective mechanisms using the skin as a primary illustration. In the nasal cavity hairs and mucus trap small particles viruses bacteria dust and. White blood cells that protect the body by.
Skin works to neutralise aggressors such as bacteria viruses and pollution and prevent them for entering. The main functions of the skin are protection barrier against ultraviolet radiation microorganisms and water loss the synthesis of vitamin D detection of sensation eg touch temperature pain and the regulation of body temperature. The use of protective equipment a skin lubricant or wet surface conditions has a positive effect on preventing abrasion-type injuries from artificial turf surfaces.
Prevents water loss from body surface. It has multiple layers of protection starting with the first layer of protection being the skull or cranium which acts as armor shielding the brain from blowsThe next layer of protection is the meninges which has three membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord to keep it from being damaged by contact with the inside of. Protection against UV light.
Human skin is repeatedly exposed to various DNA-damaging environmental influences and therefore requires numerous endogenous mechanisms to protect against reduce andor repair such damage. Protects entire body from abrasion exposure to harmful chemicals temp extremes bacterial invasion.

Wound Care Treatment Products Healing Time

A Common Bfrb Compulsive Skin Picking Bfrb Body Focused Repetitive Behavior Skin Picking Disorder

Skin 2 Accessory Structures Of The Skin And Their Functions Nursing Times

Immune System Cell Diagram Mediated Immunity Humoral Immunity Cell Diagram Immune System Nursing Immunity Nursing

L Methylfolate Mthfr Gene Article Describing What It Is And How To Use L 5 Mthf Just One Pathway In Our Genetic Makeup Methylfolate Mthfr Gene Mthfr

The Six Primary Functions Of The Skin A Brazilian Reasons 0019 Electrolysis Beauty Lounge

Role Of Skin Skin S Protective Barrier Eucerin
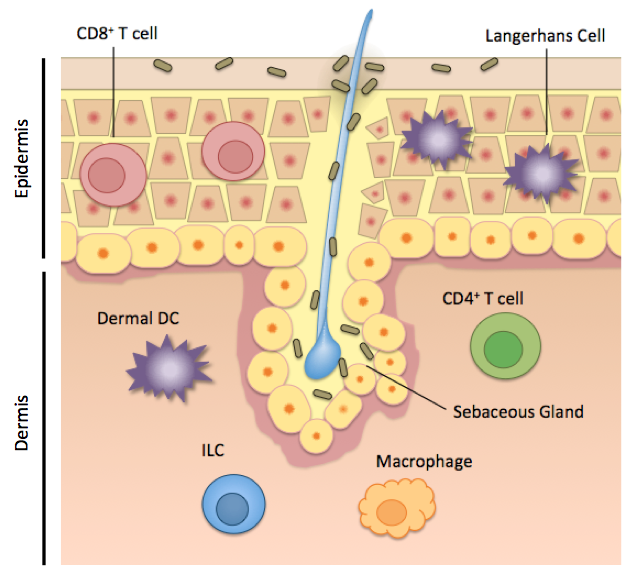
Just Skin Deep Your Immune System At The Surface Ecr Community

What Is The Stratum Corneum And Its Importance In Skin Care Skin Care Strata Skin

Stratum Corneum Top Layer Of Skin Anatomy And Function

Physical Defenses Microbiology

Structure And Function Of Skin Biology For Majors Ii

Skin 2 Accessory Structures Of The Skin And Their Functions Nursing Times

Just Skin Deep Your Immune System At The Surface Ecr Community





Comments
Post a Comment